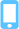
Bodyweight exercises remain central to many fitness routines due to their accessibility and functional benefits. One effective combination is the push-up plank, which merges static core engagement with dynamic upper body movement. This exercise targets multiple muscle groups, promotes better posture, and supports everyday mobility without equipment.

The plank position is an isometric exercise where the body is held in a straight line from head to heels, engaging the abdominal muscles and stabilizing muscles throughout the trunk. It reinforces spinal alignment and balance, helping maintain core stability during activities like lifting or bending. Planks also activate shoulders, arms, glutes, and legs, requiring the whole body to maintain proper alignment.
The push-up strengthens the upper body, recruiting chest, shoulder, and triceps muscles while also engaging the core for stability and alignment. Repeated push-up practice increases muscle strength and endurance by combining concentric and eccentric actions, while also improving joint coordination, balance, and overall functional movement.
A push-up plank, which moves between a plank and a push-up, combines the stabilizing benefits of the plank with the strength demands of the push-up. This compound exercise trains muscles in a way that mimics natural movements, enhancing both stability and strength.

Training Benefits and Application
- Core Stability — Even short intervals of planks, such as two to three sets of 20–60 seconds, reinforce trunk stability and improve posture.
- Upper Body Strength — Push-ups activate upper body muscles while maintaining core engagement, creating a balanced strength workout.
- Movement Control — The plank-to-push-up transition teaches coordinated body control, improving functional performance in sports or daily activities.
For beginners, mastering the static plank first is recommended. Building core strength before integrating push-ups improves form and reduces the risk of strain. Variations like side planks, high planks, and plank shoulder taps can target specific goals while keeping training diverse.
In addition to strength and stability, push-up plank routines contribute to overall movement efficiency. They encourage proper alignment and balanced muscle activation, reducing compensatory movements. These exercises can be adapted for different levels of fitness and can be performed anywhere, making them suitable for home workouts as well as gym routines.
The push-up plank continues to be valued as a versatile, equipment-free exercise that bridges core stability and upper body strength. Its combination of static and dynamic elements makes it effective for improving posture, enhancing coordination, and building functional strength. Consistent practice helps develop control, endurance, and overall body awareness, supporting a sustainable fitness routine.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What muscles does the push-up plank target?
It engages the core, shoulders, chest, triceps, glutes, and leg stabilizers, making it a full-body exercise.
2. How long should a plank be held?
Holding a plank for 20–60 seconds per set, repeated two to three times, is sufficient to improve core strength.
3. Is this exercise suitable for beginners?
Beginners can start with static planks to build foundational core strength, then progress to push-up planks.
4. Can it help posture?
Yes, strengthening the core and stabilizing muscles contributes to better spinal alignment and posture.
5. Is equipment required?
No. Push-up planks can be done anywhere without any equipment, making them convenient for home workouts.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español