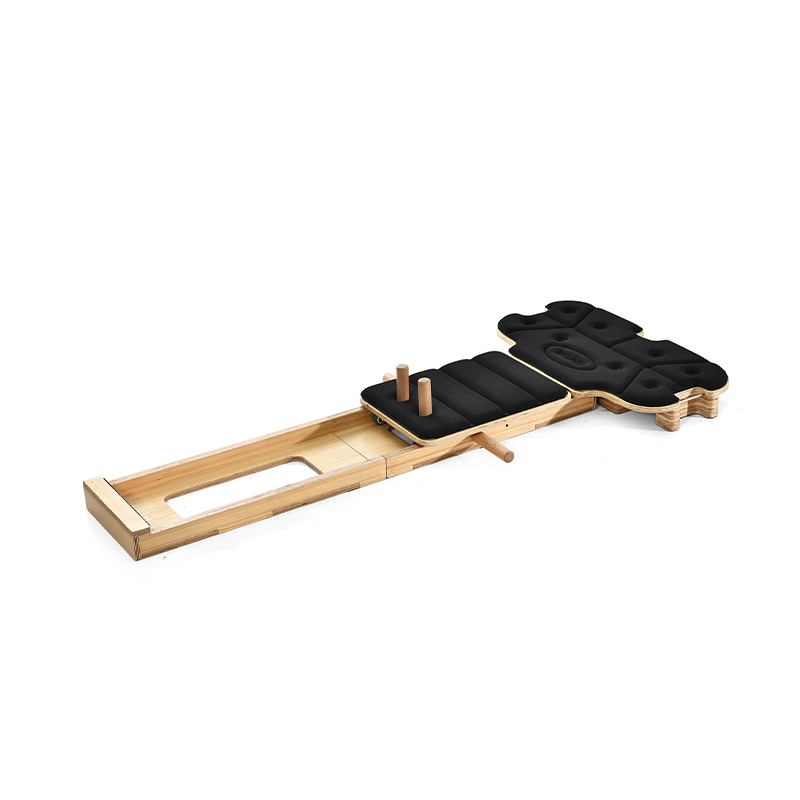
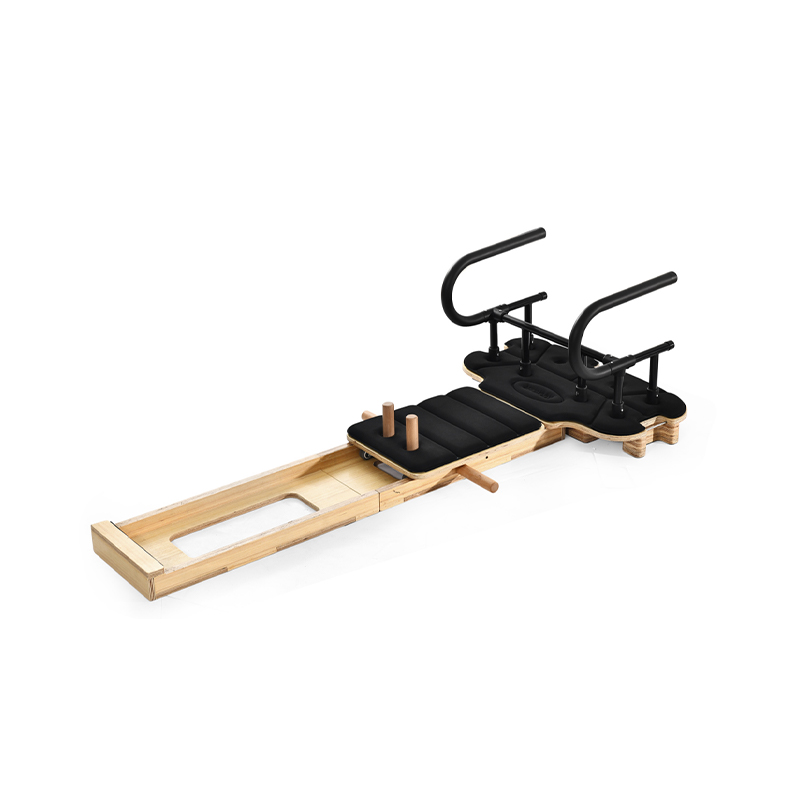
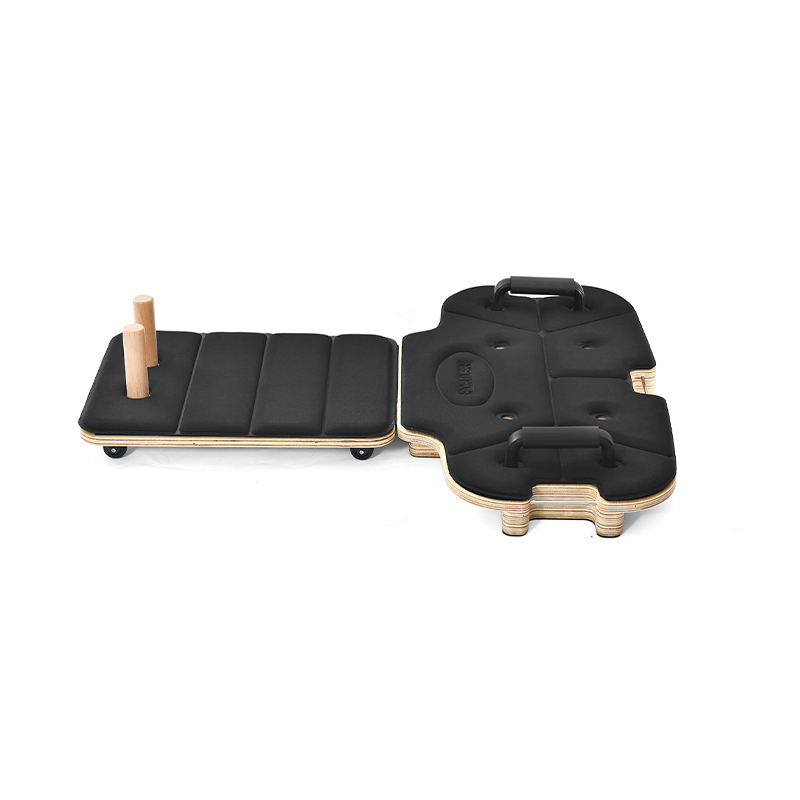
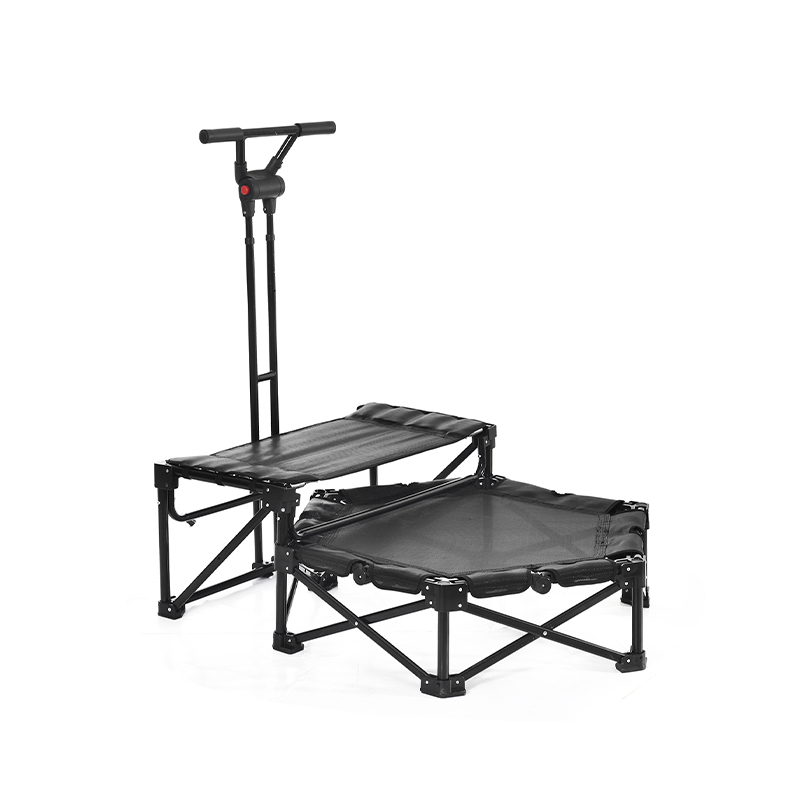
Athletic cardio squat equipment accessories are essential tools designed to improve workout effectiveness, support proper form, and increase safety during squat exercises. Squats are fundamental movements in athletic training and fitness programs, targeting major muscle groups such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core. The right accessories complement squat routines by adding resistance, providing stability, or offering feedback to optimize performance.
One common accessory is the resistance band, often used around the thighs or knees during squats. These bands add lateral resistance, encouraging proper knee alignment and activating additional muscles like the hip abductors. Incorporating resistance bands helps improve joint stability, muscle balance, and overall squat mechanics, which are crucial for injury prevention and strength development.
Weightlifting belts are another accessory frequently used during squats. These belts provide core support by increasing intra-abdominal pressure, helping stabilize the spine and reduce the risk of lower back strain. While not necessary for all users, belts can benefit those lifting heavier loads or working on improving squat form under progressive resistance.
Squat pads or cushions attach to bars or are placed on shoulders to reduce discomfort during weighted squats. These accessories help distribute pressure evenly, allowing users to focus on technique without distraction from pain or bruising. Comfort aids like these can encourage longer training sessions and more consistent progress.
Footwear also plays a vital role in squat performance. Athletic shoes designed for lifting offer firm soles, proper arch support, and a stable base. Such footwear ensures better ground contact, enhancing balance and force transfer during the squat movement. Some athletes prefer small shoes for increased foot engagement, while others choose specialized squat shoes with elevated heels for improved ankle mobility.
Platforms or mats designed for squat workouts provide a stable, non-slip surface that absorbs impact and protects joints. These accessories help maintain safety, especially in home gyms or areas with hard flooring. Additionally, adjustable squat racks and safety bars are important for supporting proper depth and safeguarding against accidents during heavy lifts.
For cardio-focused squat training, accessories like weighted vests or ankle weights can increase intensity without requiring bulky equipment. These add extra resistance to bodyweight squats or jump squats, elevating heart rate and muscular endurance. Incorporating such gear supports both strength and cardiovascular benefits, making workouts more efficient.
Proper use of these accessories involves understanding individual needs and workout goals. Beginners may start with simple resistance bands or bodyweight squats before progressing to weighted exercises with belts or vests. Experienced athletes often combine several accessories to target specific muscle groups and optimize training outcomes.
Maintenance of squat equipment accessories is important for safety and longevity. Resistance bands should be checked regularly for tears or wear, while belts and pads need cleaning to prevent odor and deterioration. Footwear requires proper care, including cleaning and sole inspection, to maintain performance and reduce injury risk.
Using accessories also requires attention to technique and body awareness. Accessories should complement—not replace—proper form and controlled movement. Working with a trainer or following instructional resources can help users integrate accessories effectively into their squat routines.
In summary, athletic cardio squat equipment accessories enhance the effectiveness, safety, and comfort of squat workouts. Whether used in a home gym or professional setting, squat accessories provide valuable support for achieving fitness goals while reducing injury risk.


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español